KVM Automation is well known for excellence in robotic systems integration. We are highly experienced in integrating a broad span of robot models from the world’s prominent manufacturers within various applications such as palletizing, welding, pick and place, collaboration, and also in the precision industry.
We can also program the ARM board through Linux OS for Radio Transmission Unit (RTU) or any IoT application by utilizing MQTT or AMQP protocols. Also, programming and troubleshooting the KUKA robotic arm with KRC2, KRC1 controllers. We use our knowledge, expertise and creativity to provide clients with the best solutions. Our team minimizes downtime at the point of installation and troubleshooting through using offline programming and a ladder logic simulator.
Robotic Systems Integration Process
The robotic systems integration process is a series of steps to create a robotic system. The steps are:
- Robot design
- Software development and implementation
- Integration testing and debugging
- User acceptance testing
Types of Robots
The most common types of robots include:
- Mobile Robots – Robots with wheels or tracks that can move freely across an area. They’re designed to travel on their own and often have multiple degrees of freedom, allowing them to pick up items, cut materials, assemble products, and more.
- Industrial Fixed-Base Robots – Fixed-base robots are stationary industrial machines used for material handling applications in manufacturing facilities. They can work in various environments, such as warehouses, assembly lines, and machine shops, where they typically move parts from one location to another as part of the production process.
- Cartesian Coordinate System – A Cartesian coordinate system describes location based on three dimensions (X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis).
Palletizing
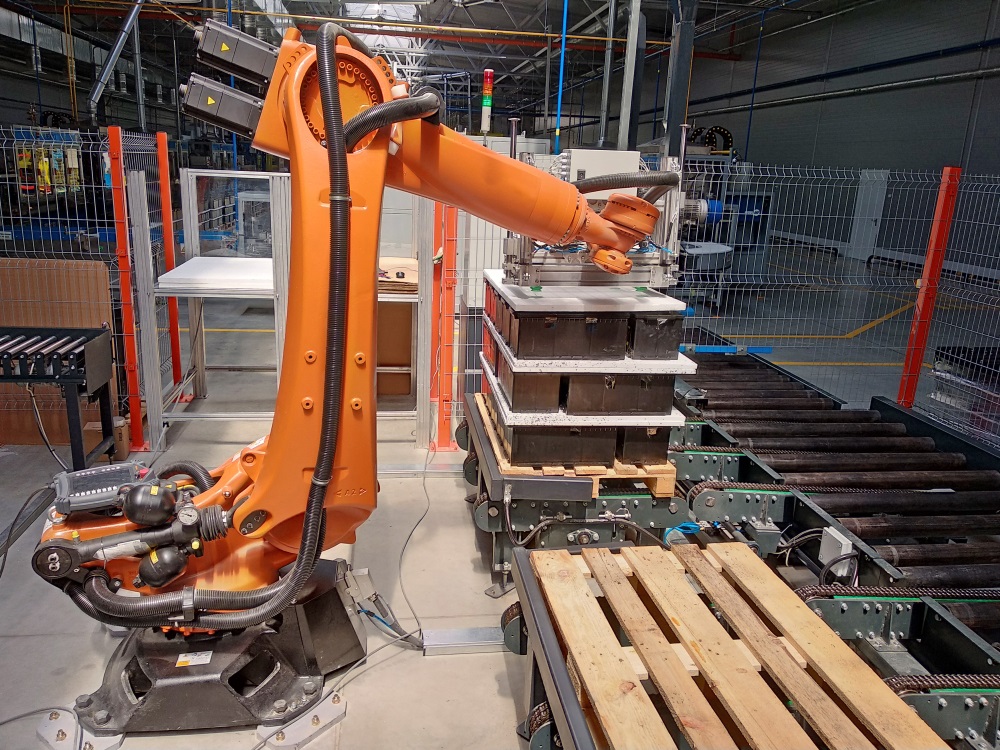

Robotic palletizing is adaptable to various products and situations. KVM Automation has designed specific grippers for a wide variety of products. KVM Automation has built systems for single and multiple lines. To form a fully integrated solution, the systems are often integrated with other equipment such as stretch wrappers. We design and build custom palletizing robotic systems integration cells to be as simple or complex as your needs require. We will review your requirements and create a solution for your custom palletizing needs.
- Open-Top display cases
- Construction materials
- Frozen food applications
- Bags up to 100 pounds
- Unsanitary applications
- Custom end of arm tooling for various odd-shaped products
- Automatic pallet dispensers
- Heavy weight products
- Pallet stretch wrappers
- Sheet application systems
- Pallet labeling systems
Robotic Case Packers
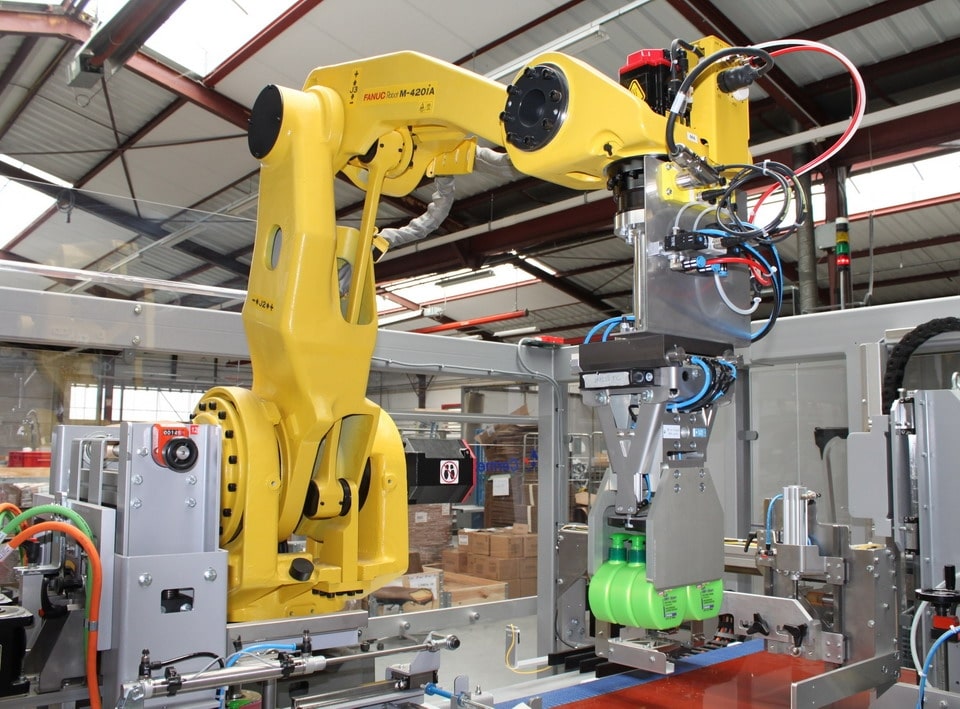

Traditional packing systems are highly limited and can lack the nuance needed for custom orders. When drop packers or wrap-around packers are restricting your shipping flow, our custom robotic systems integration packers can improve your expediency and customer satisfaction.
- Pack multiple production lines of varied products simultaneously
- Pack multiple varieties or flavors/variety into a single case
- Handle sensitive products gently
- Provide very high-speed production
- Rapid changeover from one product size to another
Inline Process
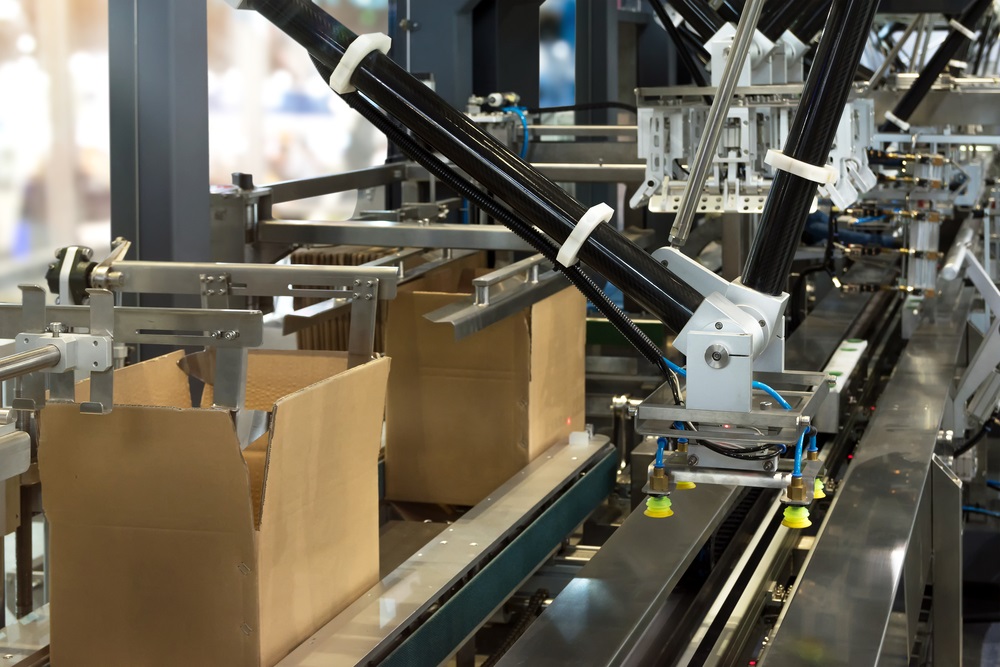

There are many steps along the way, from the initial steps to production up to final packaging. Our systems will ensure that each product of the line is inspected, measured and handled carefully to guarantee your customers the highest quality product available on the market.
Welding
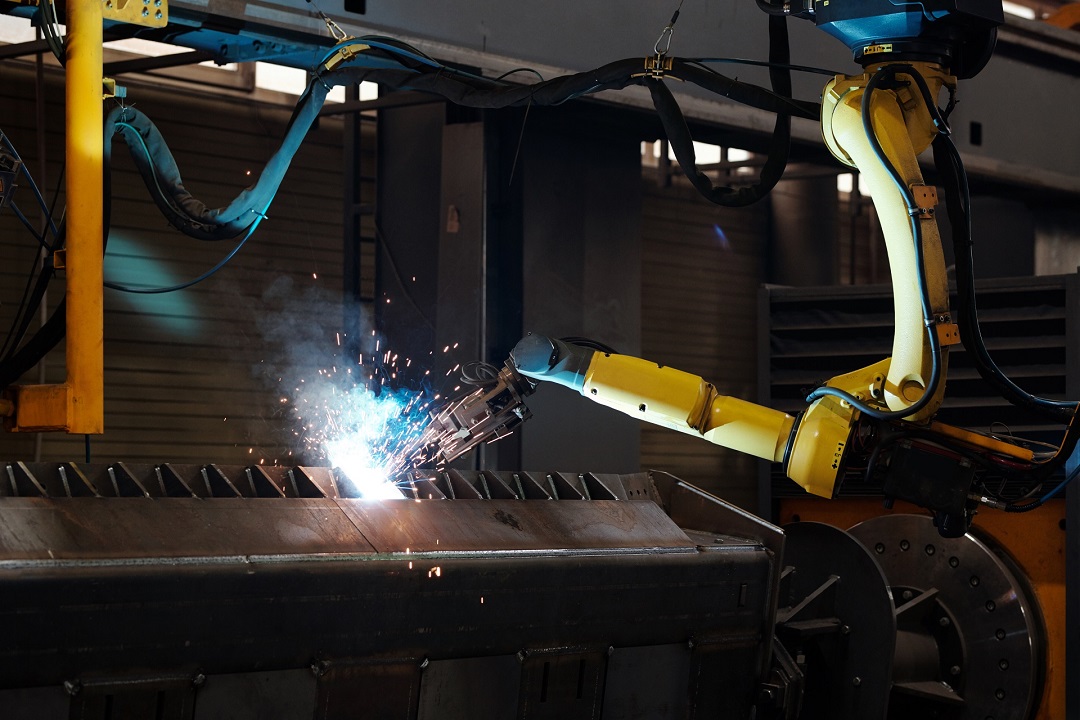

One of the most common applications for industrial robotic systems integration is welding. At KVM Automation, we have built many systems integrating a wide range of welding technologies such as Metal Inert Gas (MIG) and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG).
Pick and Place
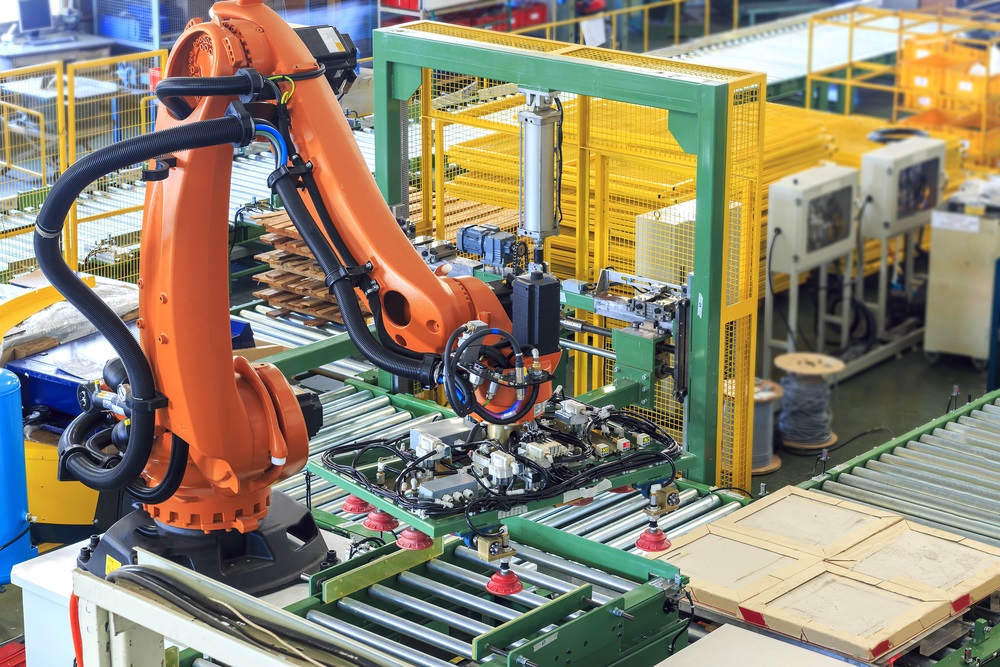

Finding, selecting, and packing the correct products into the correct packages is a job highly prone to mistakes. Properly programmed robotic systems can ensure fewer mistakes, faster packing and shipment, and more sanitary transactions. This leads to fewer returns or complaints.
On-site Robotic Programming

It seems easy but quite complex because you need to know your robot’s work and limitations before writing programs. For example, if you want your robot arm to pick up an object and move it from one location to another, the program needs to know where each part of the arm (such as the elbow) is located with respect to other parts (such as the end effector).
Robot programming is typically done using a programming language such as C++ or Java designed to develop robotics applications. It can also be done using the graphical user interface (GUI)-based design tools that provide visual representations of robots and their operations to make them easier for non-technical people such as engineers or managers.
Whether your system was installed by another company or us, we have many highly qualified technician programmers available to visit your facility. We will take a look at your system and improve performance, make adjustments for your new products or even create a new system program for your existing robotic systems.
Machine Tending*
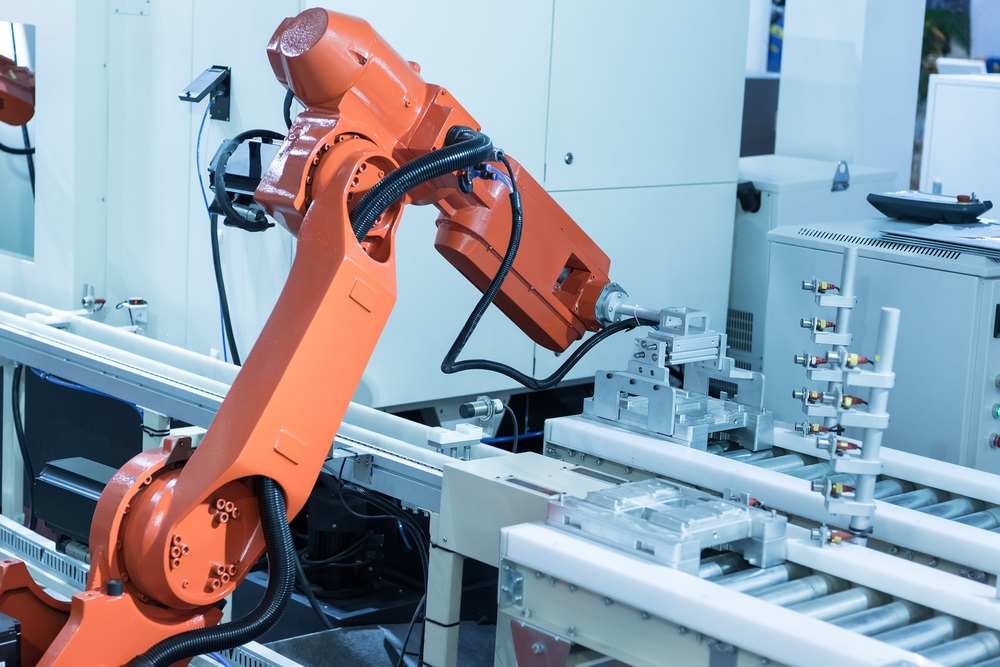

Machine Tending is an expanding application field for industrial robotic systems integration. The robot’s ability to perform both the load and unload operations and the secondary functions on the machined parts supplies an effective manufacturing solution that helps with the “Lights Out” operation.
Automation Controls
Automation controls are used to control the movement of robotic systems integration arms and grippers. These automation controls can be programmed to perform various tasks, such as picking up an object, placing it on a conveyor belt, or applying adhesive.
Some common automation controls are:
- CNC (computer numerical control) controllers – CNC controllers are used to programming automated machinery that performs repetitive manufacturing operations. For example, a CNC machine might be programmed to move parts along multiple axes while cutting them out with its laser or water jet cutter.
- PLCs (programmable logic controller) – PLCs are used in industrial settings for controlling processes like machine operation and monitoring equipment status.
Specialty End-of-Arm-Tooling (EOATs)
Specialty End-of-Arm-Tooling (EOATs) are attachments that can be mounted to the end of a robot arm. They are used for picking, placing, dispensing, welding, painting, and assembling. There are many types of EOATs available:
- Cartesian robot arms with a tool changer for 90° rotation of the axes;
- Cartesian robot arms with integrated tool changer;
- Servo mechanisms with either a mechanical or electrical connection between the servo motor and actuation mechanism;
- Direct drive linear actuators without gearing connected to a hydraulic pump through an electric motor driver (linear servomotors).
High-Speed Assembly
The high-speed assembly process is a type of manufacturing that uses automated equipment to assemble products.
High-speed assembly is measured by the number of parts it can assemble in one minute. This measure is called parts per minute (PPM), which refers to how many parts can be assembled in one minute.
Assembly and Test Systems
Assembly and Test systems are used to automate the assembly and testing of complex electronic and mechanical devices.
Robotic Assembly and Test Systems combine robotic technology, vision technology, high-precision positioning devices, communications networks, software tools, and other components into one integrated system.
The main elements of a Robotic Assembly & Test System are:
- Robot Manipulators – The robot manipulator is the end effector of a robot system with two or more degrees of freedom. It performs tasks such as picking up parts or placing them on a conveyor belt. It may also move parts over an inspection area to be visually examined through cameras, or other sensors mounted on the arm itself or elsewhere in its environment.
In today’s competitive business environments, manufacturers need to obtain a higher degree of flexibility and productivity in their manufacturing operations. To achieve this, many organizations are looking for ways to improve their process performance through automation.
Robotic systems integration is one way that companies can improve their processes by integrating robotic machines with existing equipment and/or software systems. KVM contractors offer countless solutions to improve your cycle time, reduce your labor costs and increase your work efficiency. Just fill out the form below and we’ll contact you immediately.
